
Yan Cui
I help clients go faster for less using serverless technologies.
NOTE: if you’re unfamiliar with how PostSharp works under the hood, I highly recommend that you check out Dustin Davis‘ excellent PostSharp Principles series of blog posts here.
The Problem
The new async/await keywords in C# are pretty awesome, and makes life an awful lot easier when writing asynchronous and non-blocking IO code. However, for those of us who are using frameworks such as PostSharp to deal with cross-cutting concerns we now face a new challenge – the aspects which we have come to rely upon no longer works the way we expect them to when applied on async methods (which returns void, Task or Task<T>), as can be seen from the examples below:
So what’s wrong here?
If you take a look at the code from the above example using a decompiler such as JetBrain’s DotPeek, you’ll see that the normal synchronous version of Foo looks something along the line of:
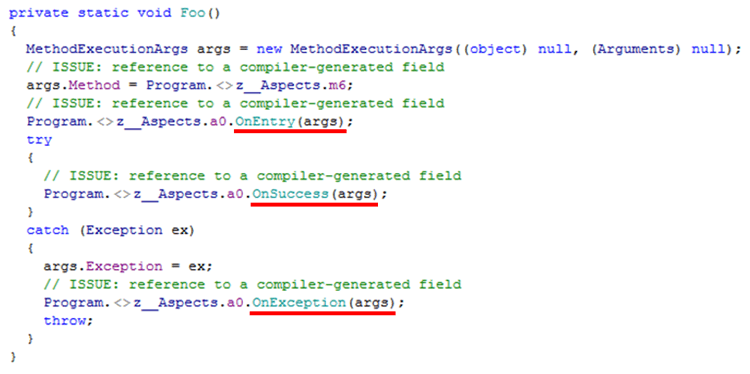
As you can see, the weaved code include calls to the OnEntry, OnSuccess and OnException methods provided by the OnMethodBoundaryAspect class, so everything is as expected here.
For FooAsync however, the picture is a little more complicated:
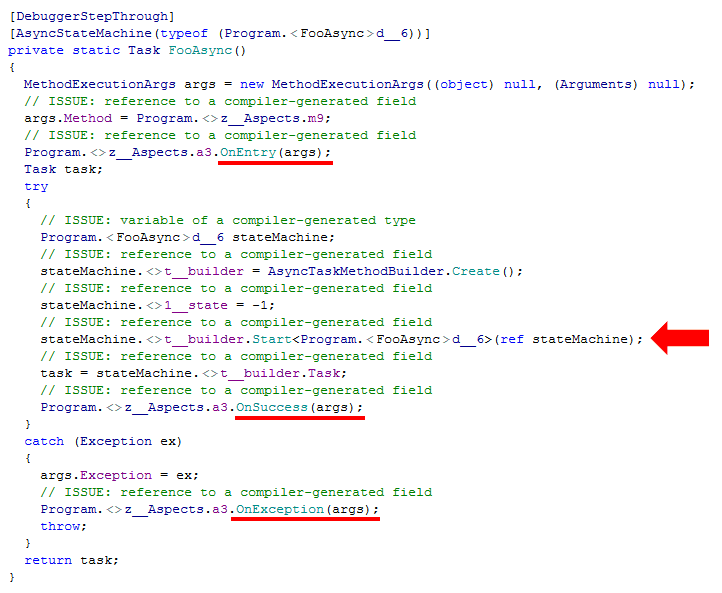
Turns out the C# compiler rewrites async methods into a state machine which means that although the OnSuccess and OnException hooks are still in place, they’re not telling us when the body of the method succeeds or fails but instead, when the state machine creation has succeeded or failed!
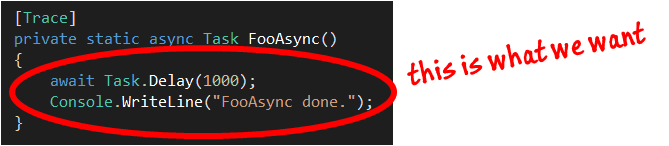

Pretty big bummer, eh?
Proposed Solution
One way (and the best way I can think of for now) to get around this is to have a special aspect which works with methods that return Task or Task<T> and hook up continuations to be executed after the returned tasks had finished. Something similar to the below will do for the on method boundary aspect:
And then you can create a TraceAsync attribute that works for async methods:
As you can see from the output above, our new OnTaskFinished, OnTaskFaulted and OnTaskCompletion hooks are correctly executed after the task returned by the async method had finished, faulted due to exception or ran to completion!
The same approach can also be applied to other built-in aspects such as the MethodInterceptionAspect class.
Before you go…
However, there are a two things you should consider first before jumping into the workaround proposed above.
1. if you look at the output from the previous example carefully, you’ll see that the line “FooAsync finished” came AFTER “Entering Boo” even though from the test code we have awaited the completion of FooAsync before calling Boo. This is because the continuations are executed asynchronously.
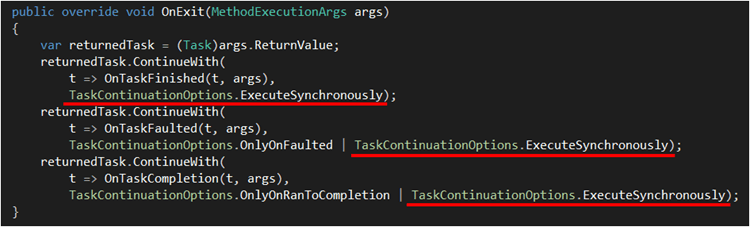
If this behaviour is not desirable to you, there is a very simple fix. Back in the OnAsyncMethodBoundAspect class we defined above, simply add TaskContinuationOptions.ExecuteSynchronously to each of the continuations:
2. the proposed solution still wouldn’t work with async methods that return void simply because there are no returned Task/Task<T> objects to hook up continuations with. In general though, you should avoid having async void methods as much as possible because they introduce some pitfalls which you really wouldn’t want to find yourself in! I’ve discussed the problem with aysnc void (and some potential workarounds) in a previous post here.
I hope this post proves useful to you, and happy PostSharp’ng! I hear some big things are coming in this space ![]()
Whenever you’re ready, here are 3 ways I can help you:
- Production-Ready Serverless: Join 20+ AWS Heroes & Community Builders and 1000+ other students in levelling up your serverless game. This is your one-stop shop for quickly levelling up your serverless skills.
- I help clients launch product ideas, improve their development processes and upskill their teams. If you’d like to work together, then let’s get in touch.
- Join my community on Discord, ask questions, and join the discussion on all things AWS and Serverless.
Nice article. Let me try and borrow the concepts here and try to apply them to the AOP done with Castle DynamicProxy and StructureMap, as detailed here – http://weblogs.asp.net/thangchung/archive/2011/01/25/aop-with-structuremap-container.aspx
Line 15 of OnAsyncMethodBoundaryAspect: Is that supposed to be ReturnType instead of ReflectedType?
Actually, I think it needs to be:
(methodInfo.ReturnType.IsGenericType && methodInfo.ReturnType.GetGenericTypeDefinition() != typeof(Task))
The return type of the method might be typeof(Task), which is never equal to typeof(Task), so you’d need to do this generic conversion.
Stupid WordPress comment cleaner thing…
There are angle brackets after the Tasks in that previous comment (I’ll put square brackets here):
(methodInfo.ReturnType.IsGenericType && methodInfo.ReturnType.GetGenericTypeDefinition() != typeof(Task[]))
The return type of the method might be typeof(Task[Foo]), which is never equal to typeof(Task[]), so you’d need to do this generic conversion.
@Joe Enos – you’re right, intellisense got the better of me there! In the version I ended up using I actually simplified it and store a bool flag so to avoid doing these checks at runtime:
protected bool IsAsync { get; set; }
public override void CompileTimeInitialize(MethodBase method, AspectInfo aspectInfo)
{
var methodInfo = method as MethodInfo;
if (methodInfo == null)
{
throw new Exception(“MethodInfo is null”);
}
IsAsync = typeof(Task).IsAssignableFrom(methodInfo.ReturnType);
base.CompileTimeInitialize(method, aspectInfo);
}
so that my attribute is compatible with both async and sync methods, and at runtime, I only hook up the task continuations for async methods, can’t share the rest of that class, but you should get the idea easy enough I suppose.