
Yan Cui
I help clients go faster for less using serverless technologies.
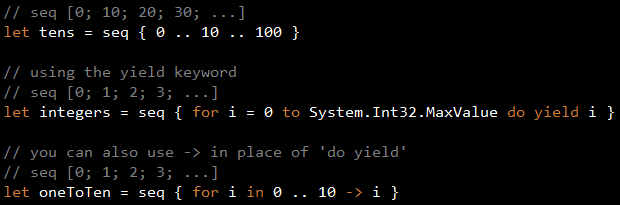
C# developers should be familiar with the yield keyword that was introduced in C# 2.0, and you’ll be pleased to know that F# also has the yield keyword which works in conjunction with F#’s equivalent of IEnumerable – sequences.
You can create sequences in F# using sequence expressions:
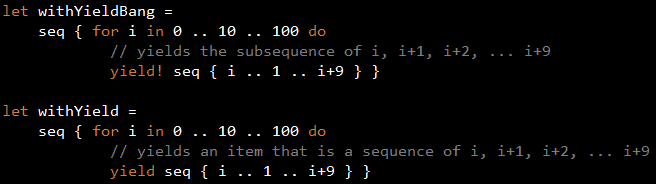
In addition, you can also use the yield! (pronounced yield bang) keyword to return a subsequence which is merged into the final sequence. Using a rather contrived example (sorry…) let’s compare the output of yield and yield!:
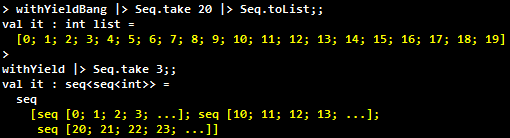
Look at how the signatures differ for these two sequences:
![]()
and how the values in the two sequences differ too:
The yield! keyword is similar to IEnumerable.SelectMany in its ability to flatten a collection of collections but it’s far more powerful as you can mix and match it with other yield/yield! statements and give you a level of expressiveness that IEnumerable.SelectMany does not.
Whenever you’re ready, here are 3 ways I can help you:
- Production-Ready Serverless: Join 20+ AWS Heroes & Community Builders and 1000+ other students in levelling up your serverless game. This is your one-stop shop for quickly levelling up your serverless skills.
- I help clients launch product ideas, improve their development processes and upskill their teams. If you’d like to work together, then let’s get in touch.
- Join my community on Discord, ask questions, and join the discussion on all things AWS and Serverless.
This detailed distinction seems to only apply to sequences? For F#’s computation expressions in general, the meaning of !-variants might differ case by case if I’m not mistaken.
for computations (see Scott Wlaschin’s excellent series if you want a detailed walkthrough of how it works – https://fsharpforfunandprofit.com/series/computation-expressions.html), you can implement both `yield` and `yield!`.
the difference is that `yield!` accepts an instance of the “wrapper type”, which in the case of the seq computation expression it means a Seq, but for other computation expressions (including your own) can be something entirely different.