
Yan Cui
I help clients go faster for less using serverless technologies.
This article is brought to you by

The real-time data platform that empowers developers to build innovative products faster and more reliably than ever before.
.Net 4 introduced the Lazy<T> type which allows you to create an object that can be lazily initialized so that you can delay the creation of large objects, for instance.
However, if your initialization logic has the potential to except at runtime (e.g. time out exceptions reading from some external data source) then you should pay close attention to which constructor you use to create a new instance of the Lazy<T> type. Depending on the selected LazyThreadSafetyMode, exceptions in the initialization code might be cached and rethrown on all subsequent attempts to fetch the lazily initialized value. Whilst this ensures that threads will always get the same result, hence removing ambiguity, it does mean that you’ve got only one shot at initializing that value…
LazyThreadSafetyMode
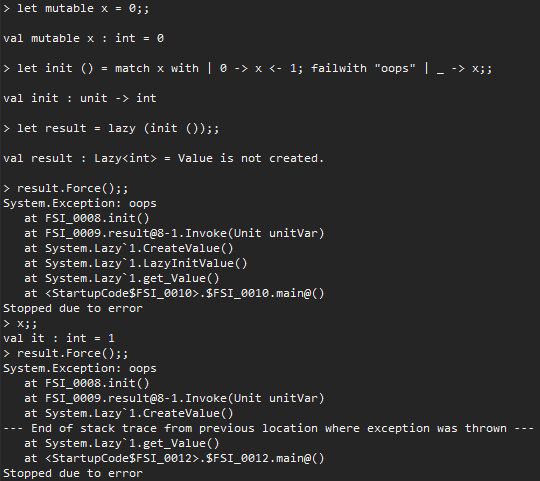
In cases where you need to be able to tolerate occasional initialization errors (e.g. reading a large object from S3 can fail from time to time for a number of reasons) and be able to try again at a second attempt, the rule of thumb is to instantiate the Lazy<T> type by setting LazyThreadSafetyMode to PublicationOnly. In PublicationOnly thread safety mode, multiple threads can invoke the initialization logic but the first thread to complete the initialization successfully sets the value of the Lazy<T> instance.
For example, the following only works under the PublicationOnly mode:
F#
F# provides a slightly nicer syntax for defining a lazy computation:
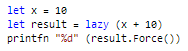
the Control.Lazy<T> type is an abbreviation of the BCL Lazy<T> type with a Force extension method which under the hood just calls Lazy<T>.Value.
Presumably the above translates roughly to the following C# code:
var x = 10;
var result = new Lazy<int>(() => x + 10);
and the thread safety mode using the Lazy(Func<T>) constructor is LazyThreadSafetyMode.ExecutionAndPublication which caches and rethrows any exceptions caught in the initialization. E.g.:
Whenever you’re ready, here are 4 ways I can help you:
- Production-Ready Serverless: Join 20+ AWS Heroes & Community Builders and 1000+ other students in levelling up your serverless game. This is your one-stop shop for quickly levelling up your serverless skills.
- Do you want to know how to test serverless architectures with a fast dev & test loop? Check out my latest course, Testing Serverless Architectures and learn the smart way to test serverless.
- I help clients launch product ideas, improve their development processes and upskill their teams. If you’d like to work together, then let’s get in touch.
- Join my community on Discord, ask questions, and join the discussion on all things AWS and Serverless.
Pingback: F# Weekly #15, 2013 | Sergey Tihon's Blog