
Yan Cui
I help clients go faster for less using serverless technologies.
This article is brought to you by

The real-time data platform that empowers developers to build innovative products faster and more reliably than ever before.
A client asked me the other day: “What happens to the running executions when I update a state machine?”
Sadly, the answer is likely that existing executions would break if you have changed the input/output of the Lambda functions they call. The solution is to use specific versions or aliases of the functions instead.
But first, let’s see what happens when you do update a state machine.
The Problem
Day 1, my state machine looks like this.
StartAt: Wait
States:
Wait:
Type: Wait
Seconds: 300
Next: Hello
Hello:
Type: Task
Resource: arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:123456789012:function:hello
Next: Decide
Decide:
Type: Choice
Choices:
- Variable: $
StringEquals: Approved
Next: Success
Default: Failed
Success:
Type: Succeed
Failed:
Type: Fail
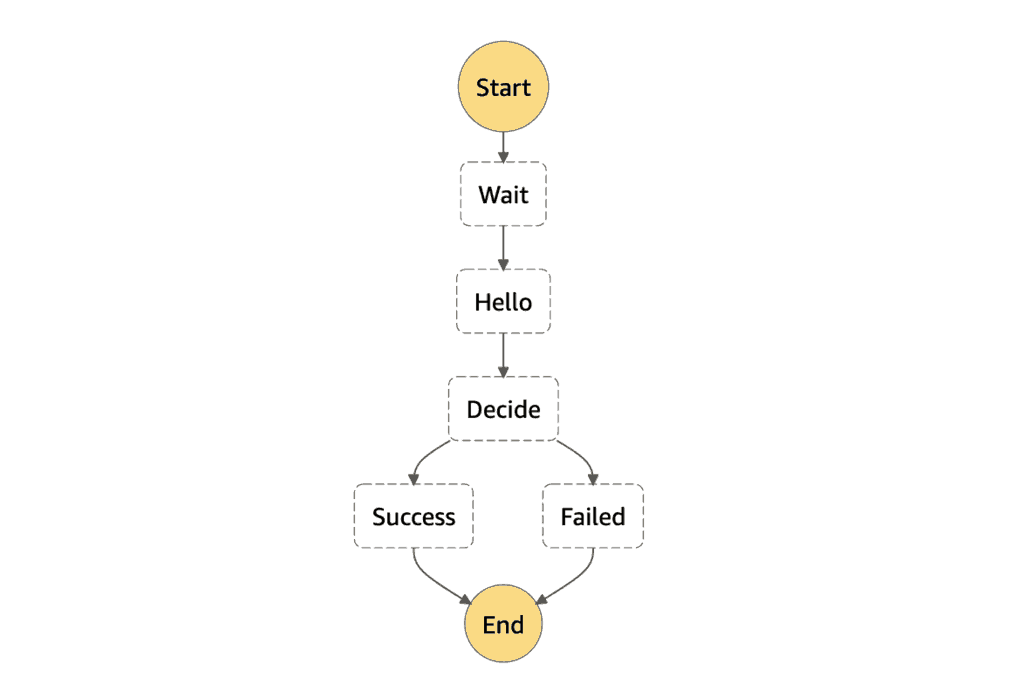
The hello function just returns “Approved” every time.
module.exports.hello = async () => {
return "Approved"
}
Day 2, we need to change “Approved” to “ThumbsUp”, and we no longer need to wait for 5 mins before giving a rating.
So we update the hello function to return “ThumbsUp”.
module.exports.hello = async () => {
return "ThumbsUp"
}
And we update the state machine definition accordingly:
StartAt: Hello
States:
Hello:
Type: Task
Resource: arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:123456789012:function:hello
Next: Decide
Decide:
Type: Choice
Choices:
- Variable: $
StringEquals: ThumbsUp
Next: Success
Default: Failed
Success:
Type: Succeed
Failed:
Type: Fail
Now it’s time to deploy the update.
Oh, wait! There is already an execution running. What’s going to happen to this execution if we deploy the update?
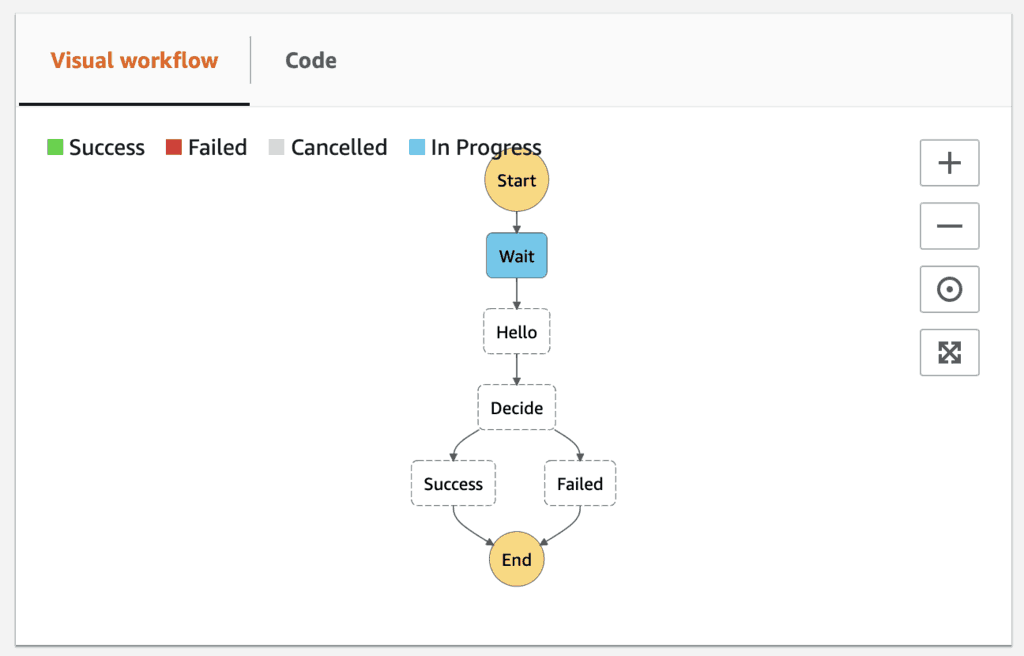
The good news is that changes to the state machine definition would not impact the state machine definition of running executions. Existing executions would continue along with their original design.
The bad news is that everything else it depends on could have changed. These include the Lambda functions it needs to call and its IAM role. In our case, the existing execution would not receive an “Approved” message when it eventually calls the hello function. It would, therefore, transition to the Failed state as the result of the changes to the hello function.
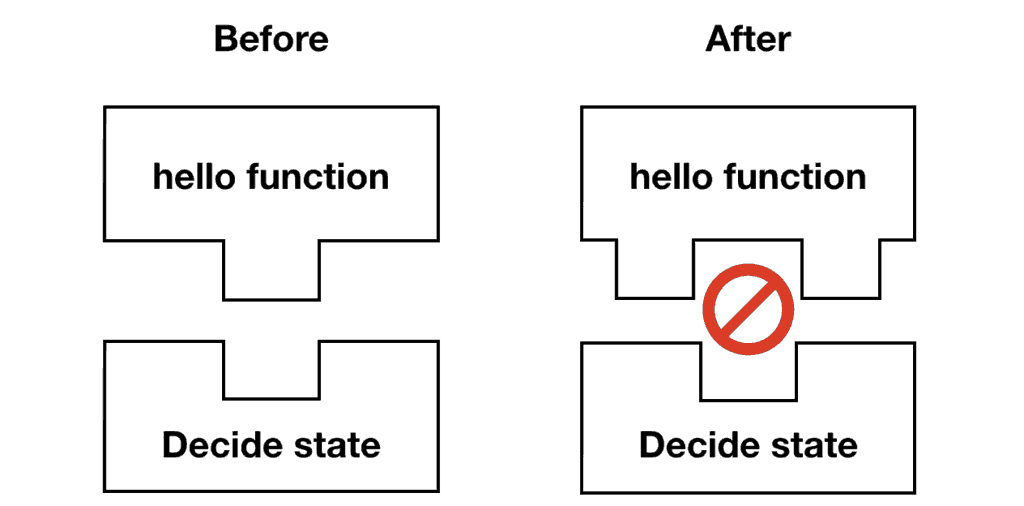
Instead, can we tie existing executions to the version of hello functions that they were created with?
The Solution
You can invoke a specific version or alias of a function by appending the version number or alias to its ARN. For example, version 2 of the hello function is at arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:123456789012:function:hello:2.
Since versions are immutable, we can ensure that existing executions would always run against the correct versions of our code.
We also need to make sure the state machine’s IAM role has the necessary permissions. Since all current and future executions would share the same role (which is a whole other problem…), it’s best to grant lambda:InvokeFunction permission for all versions. For example:
Effect: Allow Action: lambda:InvokeFunction Resource: - arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:123456789012:function:hello - arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:123456789012:function:hello:*
Ok, let’s see this in action. I published a demo project, you can check out the source code on GitHub here.
The Demo
With the Serverless framework, it’s not easy to find the function versions. Because the AWS::Lambda::Version resources have randomized logical IDs.
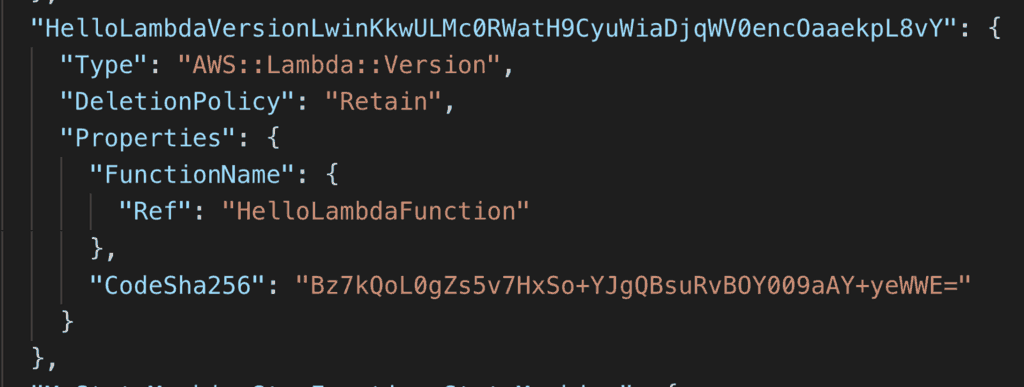
Fortunately, the serverless-step-functions plugin is able to do the legwork for us. All we have to do is to say useExactVersion: true in our state machine.
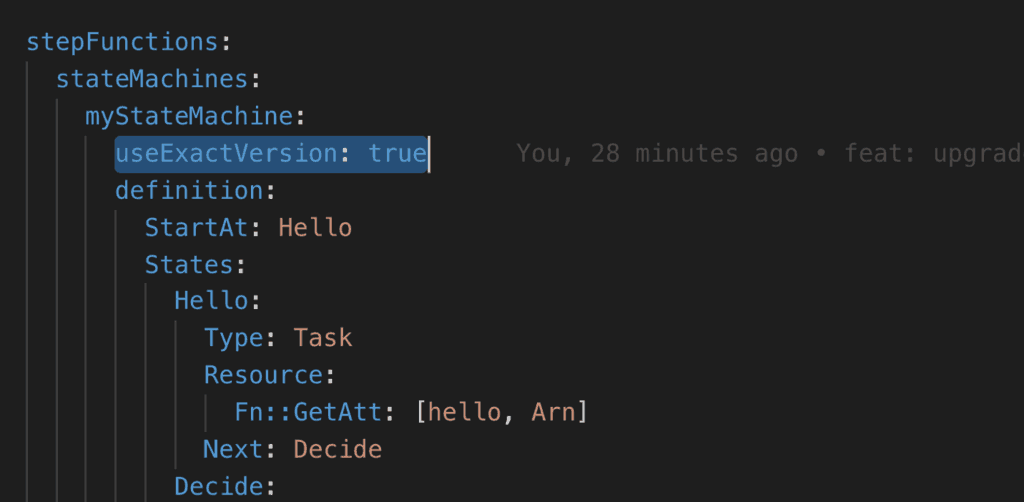
The plugin also generates the correct IAM roles (as explained above) for us too. Once deployed, the state machine definition would reference the correct resource ARN.
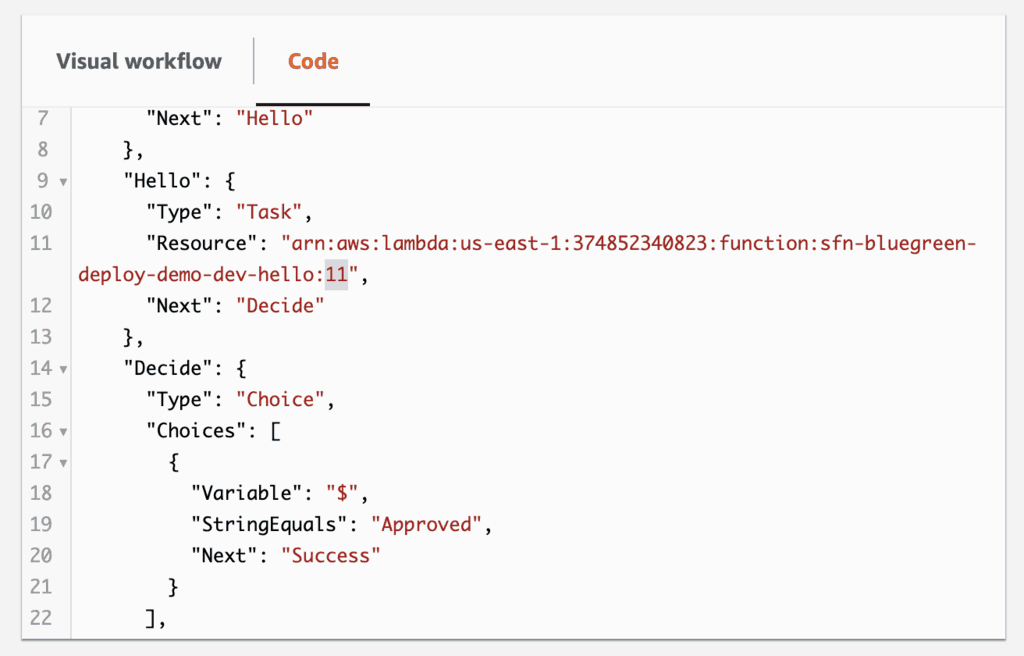
I would start an execution of the state machine. The initial Wait state gives me 5 mins to update the state machine and hello function!
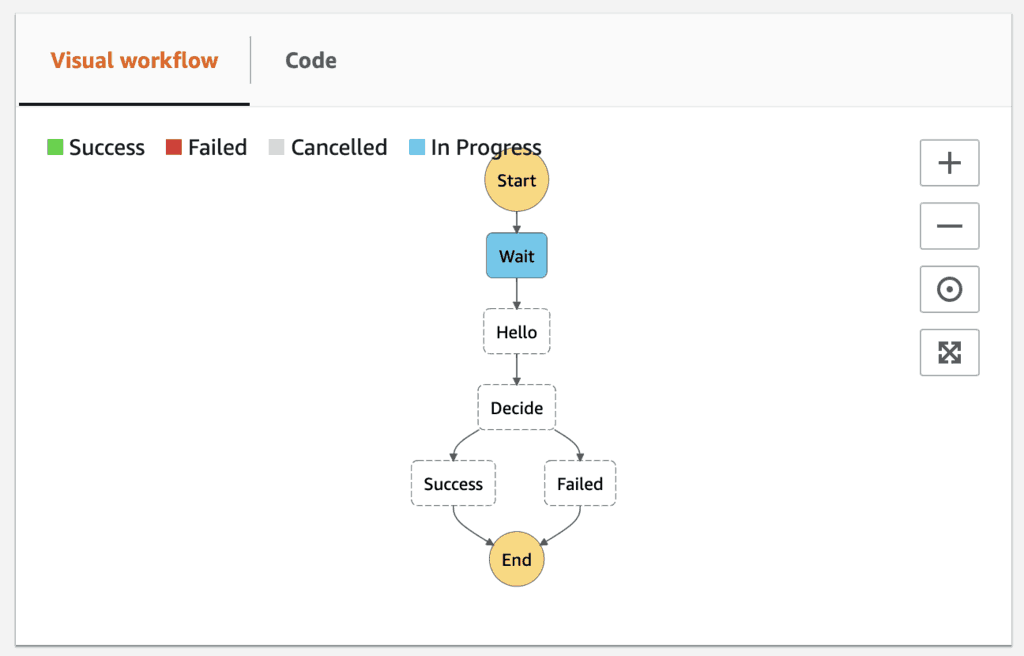
Now quickly switch to the v2 branch and run sls deploy to deploy the update. The hello function would now return ThumbsUp instead, and the state machine has also been updated.
Once deployed, notice that the Resource ARN for the Hello state is now pointing at the new version. And the Decide state is now looking for the string value ThumbsUp instead of Approved.
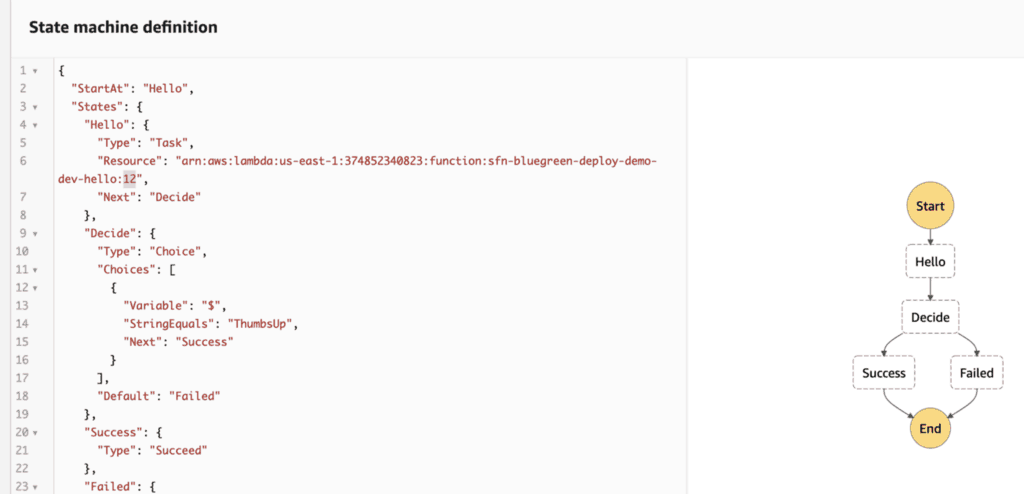
If we start another execution, it will complete successfully right away.
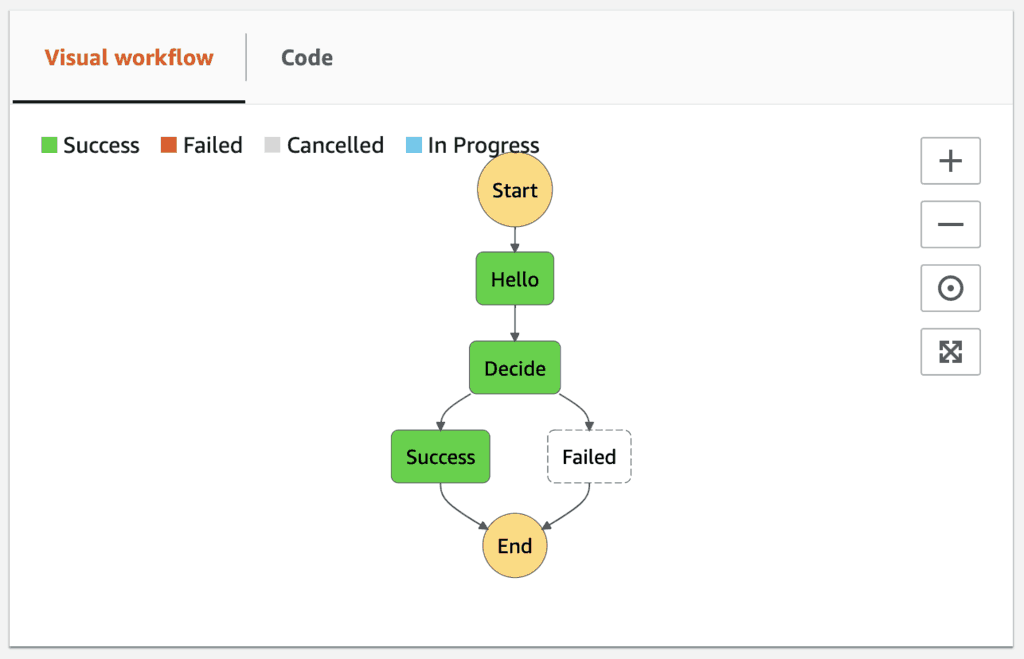
But if we go back to the Step Functions console, we can see the first execution is still running because of the original Wait state.
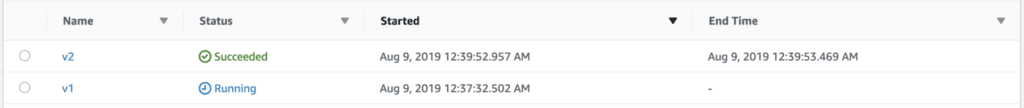
After some time, the execution comes out of the Wait state and transitions to the Hello state where it’s still looking for the string value of Approved. But since the state invokes the earlier version of the hello function, everything still worked as expected.
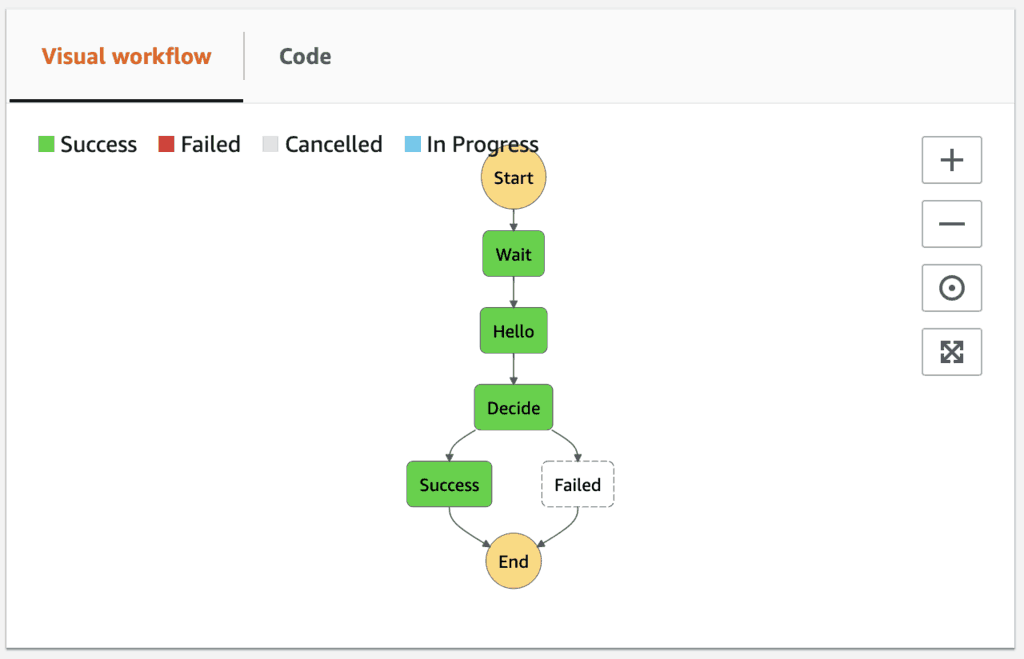
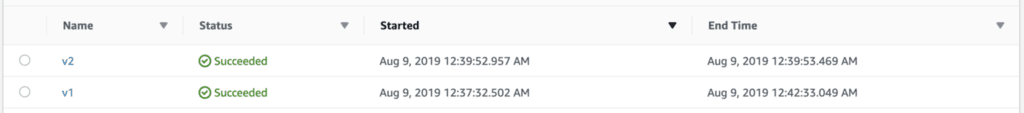
Both executions completed successfully despite us changing the return value on the hello function.
Whenever you’re ready, here are 4 ways I can help you:
- Production-Ready Serverless: Join 20+ AWS Heroes & Community Builders and 1000+ other students in levelling up your serverless game. This is your one-stop shop for quickly levelling up your serverless skills.
- Do you want to know how to test serverless architectures with a fast dev & test loop? Check out my latest course, Testing Serverless Architectures and learn the smart way to test serverless.
- I help clients launch product ideas, improve their development processes and upskill their teams. If you’d like to work together, then let’s get in touch.
- Join my community on Discord, ask questions, and join the discussion on all things AWS and Serverless.
