
Yan Cui
I help clients go faster for less using serverless technologies.
This article is brought to you by

The real-time data platform that empowers developers to build innovative products faster and more reliably than ever before.
Problem
Starting with 1 and spiralling anticlockwise in the following way, a square spiral with side length 7 is formed.
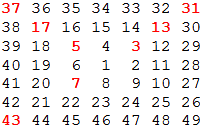
It is interesting to note that the odd squares lie along the bottom right diagonal, but what is more interesting is that 8 out of the 13 numbers lying along both diagonals are prime; that is, a ratio of 8/13
62%.
If one complete new layer is wrapped around the spiral above, a square spiral with side length 9 will be formed. If this process is continued, what is the side length of the square spiral for which the ratio of primes along both diagonals first falls below 10%?
Solution
let hasDivisor(n) =
let upperBound = int(sqrt(double(n)))
[2..upperBound] |> Seq.exists (fun x -> n % x = 0)
let isPrime(n) = if n = 1 then false else not(hasDivisor(n))
// define function that returns the number on the corners of a spiral of length n
let getCornerNumbers n =
match n with
| 1 -> [1]
| _ when n % 2 = 0 -> []
| _ -> [3..-1..0] |> List.map (fun n’ -> n*n – n’*(n-1))
let answer =
let mutable cornerNumbers, primeNumbers, size = 0, 0, 1
let mutable continueLoop = true
while continueLoop do
// get the numbers that appear at the corners of a spiral of the given size
let newNumbers = getCornerNumbers size
// increment the totals
cornerNumbers <- cornerNumbers + newNumbers.Length
primeNumbers <- primeNumbers + (newNumbers |> List.filter isPrime |> List.length)
let ratio = double(primeNumbers) / double(cornerNumbers)
if ratio < 0.1 && size > 1 then continueLoop <- false else size <- size + 2
size
[/code]
UPDATE: Having stumbled upon some very good algorithms for generating prime number sequence here, I decided to revisit my solution here and using the PGSimple3 algorithm the new code now runs in seconds!
// generate all prime numbers under <= this max let max = 100000 // initialise the list with 2 which is the only even number in the sequence let mutable primeNumbers = [2] // only check the prime numbers which are <= the square root of the number n let hasDivisor n = primeNumbers |> Seq.takeWhile (fun n’ -> n’ <= int(sqrt(double(n)))) |> Seq.exists (fun n’ -> n % n’ = 0)
// only check odd numbers <= max let potentialPrimes = Seq.unfold (fun n -> if n > max then None else Some(n, n+2)) 3
// populate the prime numbers list
for n in potentialPrimes do
if not(hasDivisor n) then primeNumbers <- primeNumbers @ [n]
// use the same hasDivisor function instead of the prime numbers list as it offers
// far greater coverage as the number n is square rooted so this function can
// provide a valid test up to max*max
let isPrime n = if n = 1 then false else not(hasDivisor(n))
// define function that returns the number on the corners of a spiral of length n
let getCornerNumbers n =
match n with
| 1 -> [1]
| _ when n % 2 = 0 -> []
| _ -> [3..-1..0] |> List.map (fun n’ -> n*n – n’*(n-1))
let answer =
let mutable cornerNumbers, primeNumbers, size = 0, 0, 1
let mutable continueLoop = true
while continueLoop do
// get the numbers that appear at the corners of a spiral of the given size
let newNumbers = getCornerNumbers size
// increment the totals
cornerNumbers <- cornerNumbers + newNumbers.Length
primeNumbers <- primeNumbers + (newNumbers |> List.filter isPrime |> List.length)
let ratio = double(primeNumbers) / double(cornerNumbers)
if ratio < 0.1 && size > 1 then continueLoop <- false else size <- size + 2
size
[/code]
Whenever you’re ready, here are 4 ways I can help you:
- Production-Ready Serverless: Join 20+ AWS Heroes & Community Builders and 1000+ other students in levelling up your serverless game. This is your one-stop shop for quickly levelling up your serverless skills.
- Do you want to know how to test serverless architectures with a fast dev & test loop? Check out my latest course, Testing Serverless Architectures and learn the smart way to test serverless.
- I help clients launch product ideas, improve their development processes and upskill their teams. If you’d like to work together, then let’s get in touch.
- Join my community on Discord, ask questions, and join the discussion on all things AWS and Serverless.