Yan Cui
I help clients go faster for less using serverless technologies.
Series:
- Algae
- Pythagoras Tree
- Cantor Dust
- Koch Curve
- Sierpinski Triangle
- Dragon Curve (this)
- Fractal Plant
Last time out we implemented the Sierpinski Triangle example from the L-System wikipedia page. Now, let’s continue our journey and see how we can implement the (rather impressive sounding) Dragon Curve example in Elm.
Example 6 : Dragon Curve
First, let’s define our L-System:

Again, thanks to the work we did in Part 4, our work here is rather simple:
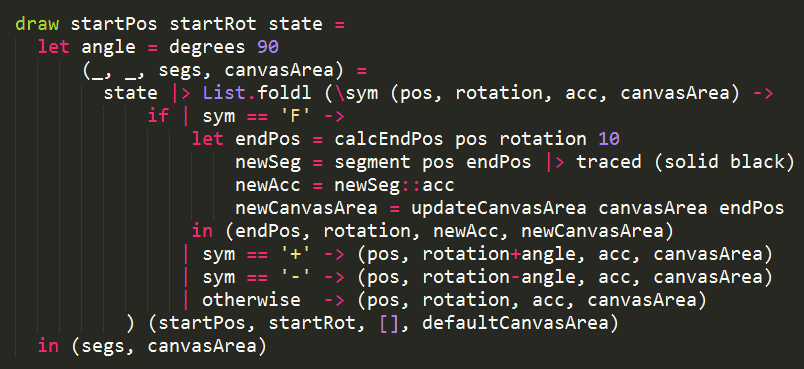
which is a pretty straight translation of:
- ‘F’ : draw forward
- ‘–’ : turn left 90 degrees
- ‘+’ : turn right 90 degrees
- ‘X’ and ‘Y’ : ignore
Unlike the other L-Systems, this one grows much slower and as it slows it does make a nice picture!
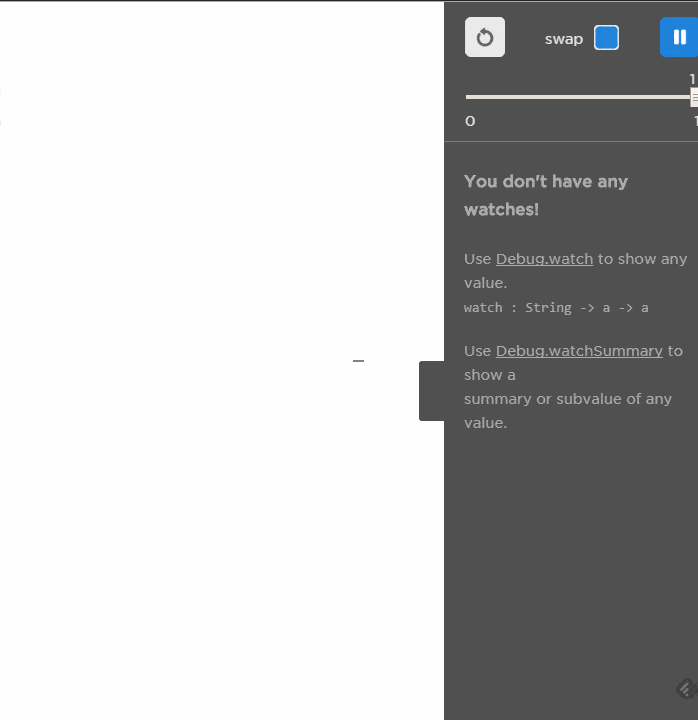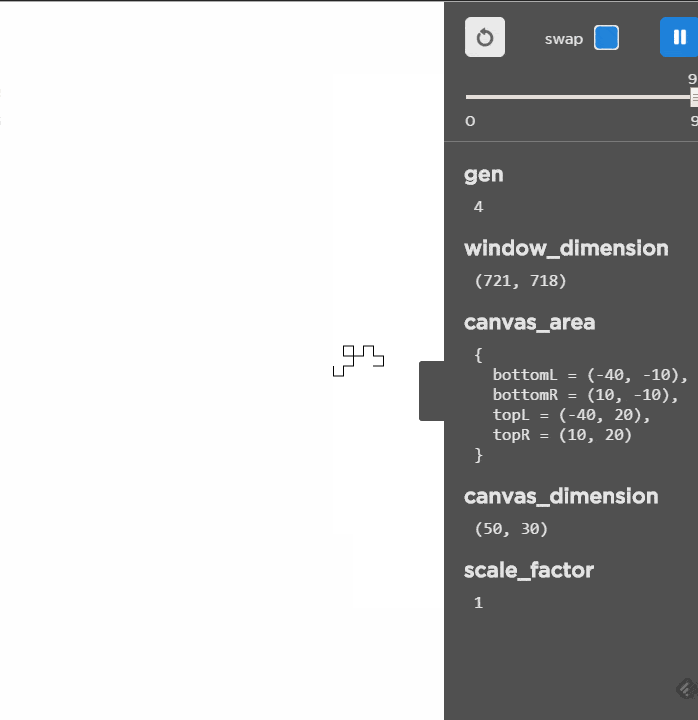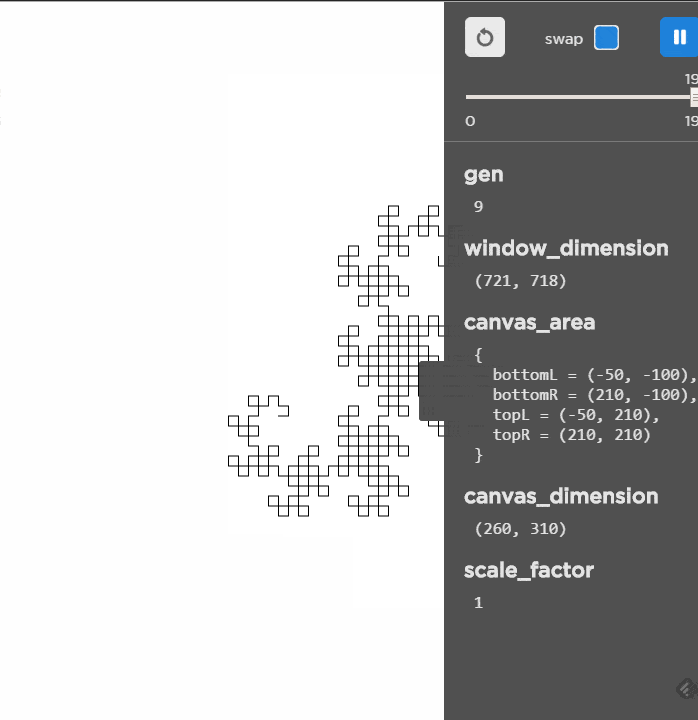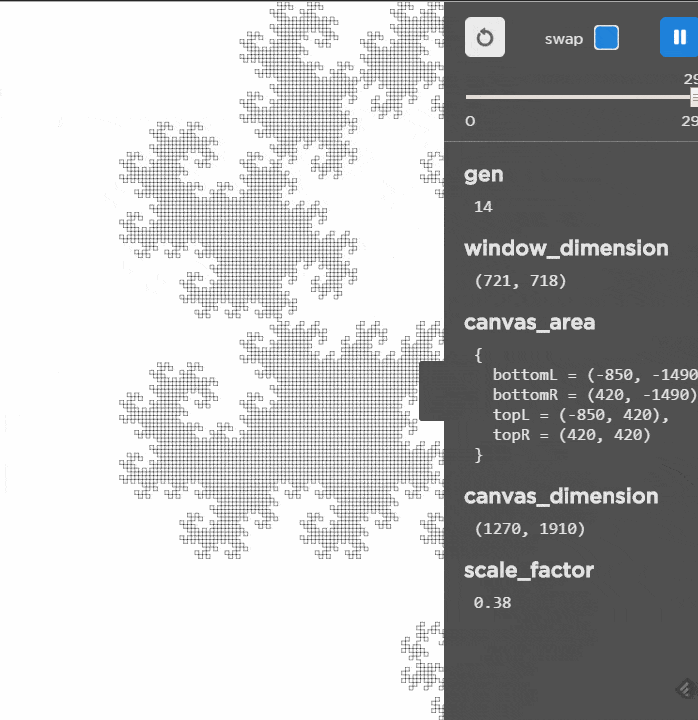
Live Demo (here)
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to evolve/devolve the L-System.
Source Code (here)
Next : Fractal Plant
Links
Whenever you’re ready, here are 3 ways I can help you:
- Production-Ready Serverless: Join 20+ AWS Heroes & Community Builders and 1000+ other students in levelling up your serverless game. This is your one-stop shop for quickly levelling up your serverless skills.
- I help clients launch product ideas, improve their development processes and upskill their teams. If you’d like to work together, then let’s get in touch.
- Join my community on Discord, ask questions, and join the discussion on all things AWS and Serverless.